Internet emailing list services — “listserves” — are an excellent way for birders to spread the word about what’s being seen in the area, and useful information about how to get there, which tree it was sitting in last, and which landowners show up with cookies and which with a shotgun. But a birder cannot live by list-serve alone. Sometimes I forget this, or get too wrapped up in the “art birds” in the studio, and not the real birds that are out there which inspire them.
So Sunday, though it was very wet at times because of a robust late winter storm that’s bringing snow to Arizona’s peaks and rain to its deserts (=wildflowers!!!), E and I went to view Da Boids at the Salt River east of the east end of Tempe Town Lake, otherwise known as “Tempe Marsh”. We went with friends who get out more than we do, which was a good thing because there was a surprise there I wouldn’t have given a second look at without a knowledgeable nudge in the ribs.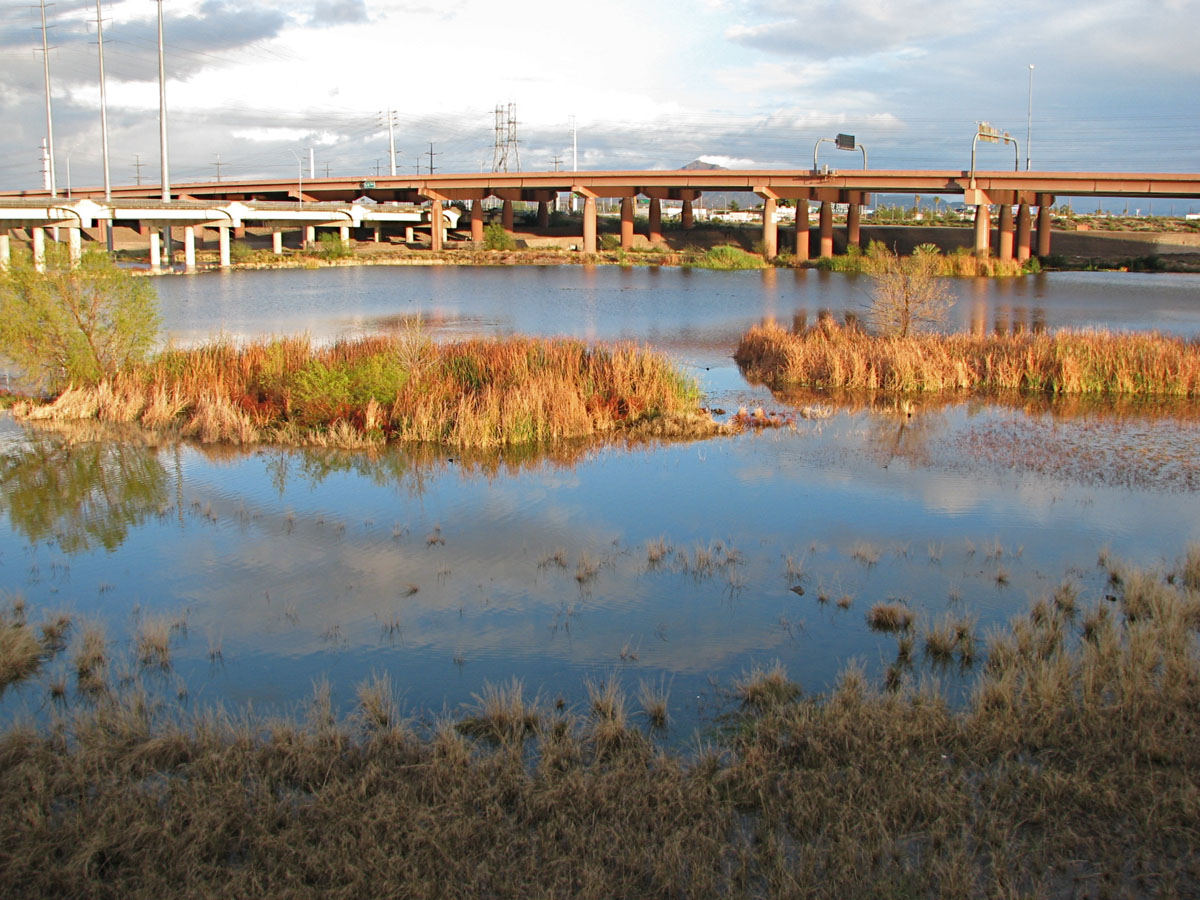
For those who aren’t familiar with it, Tempe Town Lake is a stretch of the Rio Salado (or Salt River, the jugular of Phoenix) on the northern edge of the city of Tempe, just east of Phoenix and south of Scottsdale. In the late 1990’s, engineers took the unusual action of damming the Salt at two places with huge black inflatable rubber tubes stretched from bank to bank. (The fall of the river is so flat here, that putting in just a downstream dam wouldn’t create usable depth.) The dams take advantage of a “gaining” stretch of the Rio Salado. At this point underground river water is naturally forced to the surface by bedrock (ASU’s A-Mountain and other visibly hard features jutting up out of the flatlands) and the dam slows this water and pools it together with added recycled water. The combination of human engineering and natural geology enable what on the surface often appears to be a feeble desert river to create a body of water significant enough to allow the public to fish, boat, scull, and reflect on the unappealing commercial buildings the City of Tempe has blighted A-Mountain with. If you remember the area from earlier days, it’s quite a change to the scenery to drive by downtown Tempe on the elevated Loop 202 freeway and see its bridges and buildings reflected in sun-catching wavelets.
One of the activities enhanced by this sudden advent of standing water is birding. Or, to be less anthropocentric, the new lake created habitat which has attracted a good number of waterbirds, waders, and shorebirds, as well as raptors and some landbirds (in the willows and cottonwoods that seem to spring up nearly overnight). All these in turn have attracted birders.
It’s drive-up birding, and definitely not pastoral. It isn’t quite as gritty as birding the landfill or most sewage lagoons, but it’s not wilderness. It’s very….suburban. With the sun at your back you stand at the edge of the parking lot for the mega retail complex called Tempe Market Place (hereafter TMP). It’s necessary to block out the piped-in pop music drifting across the asphalt from the shops, and to try to ignore the inviting odors of grilling carne asada telling you that your breakfast was only oatmeal, and really early in the morning. On an afternoon visit, you may vie for parking with movie-goers, and Fridays are the worst — the scene includes local bands playing at “the District”, the “lifestyle” part of the outdoors retail vortex. The most obvious features of the landscape, though, are the roads: the Mill Avenue bridges, placed at the historic Rio Salado ford and Hayden Ferry crossing (for many years the only crossing on the Salt in Phoenix), and the the raised causeway portion of the Loop 202, the Red Mountain Expressway, looming over everything. The sound of traffic is sometimes hard to hear birds over. And bring a scope, because most of the birds are at a distance.
But there are birds to see. Double-crested and a few Olivaceous cormorants are everywhere: flying in and away in skeins, hung out to dry in drowned snags (photo right), swimming with just head and neck exposed. An Osprey cruises by, then a Red tailed hawk, and a Belted kingfisher barrels thorugh, rattling. There are sandpipers, and killdeer, and coots and their more colorful cousins, Common moorhens; red-winged blackbirds and grackles; grebes of two species; egrets and herons; a group of Rough-winged swallows passing through. And there are ducks: Gadwall and Mallards, tons of Shovellers, and teal.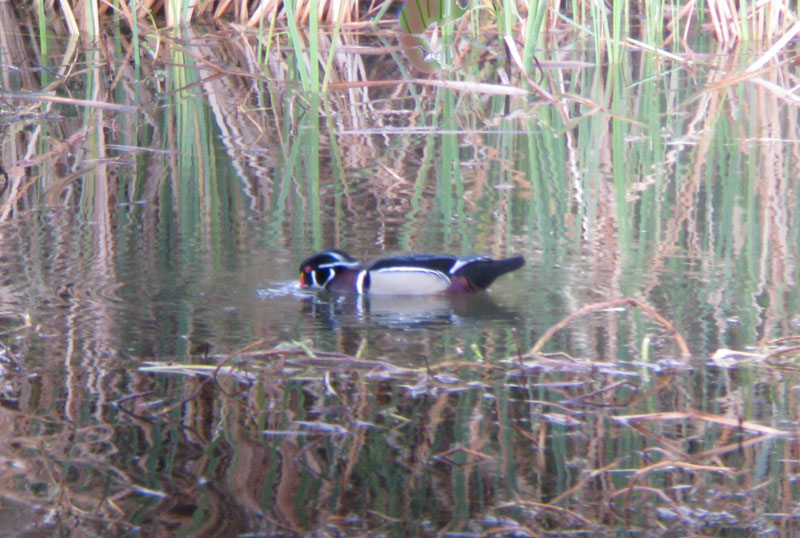  This morning a pair of ornately plumaged drake Wood ducks (one seen in photo left) are floating together in and out of the cattails, looking exotic although they are not uncommon in the winter here, and breed elsewhere in the state.
This morning a pair of ornately plumaged drake Wood ducks (one seen in photo left) are floating together in and out of the cattails, looking exotic although they are not uncommon in the winter here, and breed elsewhere in the state.
What keeps birders coming here, though, are the occasional surprises. Sunday’s surprise (at least, to me — the others were looking for it since it’s been observed in this location at least since January) was a long-distance visitor hanging with the local Green winged teal: a Common or Eurasian teal, Anas crecca. This is a bird that should be in Japan in winter, or in Turkey, not Tempe. Remember Bugs Bunny’s “I shoulda toined left in Albuquoykee?” These things sometimes happen with migratory species; they get blown around, or take a wrong turn. But I was glad our friends were on top of things, and pointed out the different field marks, because they’re subtle enough so that at a distance I easily skipped over them.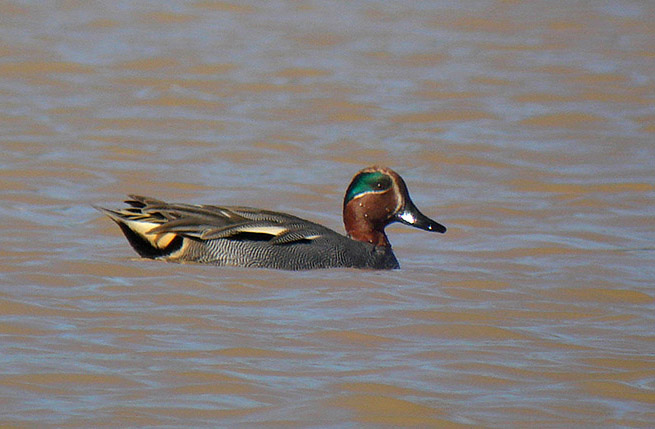 Our bird was too distant to photo, so to the right is a photo by Michael Moore of an individual seen last year at the Gilbert Water Ranch, not too far from Tempe Marsh. Since a picture’s worth 1K words, I’ve also included below a photo by ASU prof Pierre Deviche of a local Green-winged teal for you to compare: note the prominent vertical breast bar on the side of the local teal, and the more prominent white head lines on the Common teal.
Our bird was too distant to photo, so to the right is a photo by Michael Moore of an individual seen last year at the Gilbert Water Ranch, not too far from Tempe Marsh. Since a picture’s worth 1K words, I’ve also included below a photo by ASU prof Pierre Deviche of a local Green-winged teal for you to compare: note the prominent vertical breast bar on the side of the local teal, and the more prominent white head lines on the Common teal.
For you sticklers for accuracy, I should note that although I’ve called this a “life bird” sighting for me, technically it isn’t: the two birds, our local Green-winged teal and the Common teal, are currently considered by American authorities to be sub-species of the same species, Anas crecca. But the taxonomists may be about to split them, so I hear, and I’ll be ready!
Until then, I’ll just have to be inspired by seeing the two together, and add Green-winged teal to my “list” of birds-I-make-art-from, which is low on ducks at the moment. Because who can resist that cinnamon-and-green noggin?
Photos: Top, Tempe Marsh and the Loop 202, by E. Shock. #2: Great egret in the cattails, Tempe Marsh, E. Shock. #3, Cormorants drying, Tempe Marsh, by E. Shock. #4, Wood duck drake in cattails, Tempe Marsh, A. Shock. #5: Common teal at Gilbert Water Ranch, by Michael Moore. #6, Green-winged teal at Gilbert Water Ranch, by Pierre Deviche.
 Some years, one or two are found wintering or in transition on desert lakes around and about the state. They are categorized as “casual” here. This winter (Dec. ’08), there was a handful of female or immature-type Black scoters (white cheek patches) seen along the Colorado River near Parker Dam, and a White-winged scoter at Kearney Lake east of Phoenix (Jan. ’09; white cheek patches and white on the wings).
Some years, one or two are found wintering or in transition on desert lakes around and about the state. They are categorized as “casual” here. This winter (Dec. ’08), there was a handful of female or immature-type Black scoters (white cheek patches) seen along the Colorado River near Parker Dam, and a White-winged scoter at Kearney Lake east of Phoenix (Jan. ’09; white cheek patches and white on the wings).